-
E-mail
2881068607@qq.com
-
Phone
18721098757
-
Address
No. 253 Yulu Road, Jiading District, Shanghai
Ankerui Electric Co., Ltd
Enterprise level source network load storage collaboration solution
- Model
- Nature of the Manufacturer
- Producers
- Product Category
- Place of Origin
1、 Overview-Enterprise level source network load storage collaboration solution
Under the strong driving force of the "dual carbon" target, enterprises are facing a dual test of rising energy costs and urgent emission reduction tasks. The old model that relied heavily on traditional power grids and had a relatively single energy consumption structure has become increasingly difficult to adapt to the current development trend. At this time, microgrids are gradually emerging as the core strategy for enterprises to achieve the comprehensive goal of "reducing costs, improving efficiency, and achieving low-carbon", thanks to their flexible networking characteristics, intelligent regulation methods, and powerful clean energy integration capabilities. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA)Prediction: Until 2030,The microgrid market in the industrial and commercial sector is expected to grow rapidly, surpassing the $30 billion mark.
So, how can companies use microgrid technology to rebuild their energy systems? What is the core path and its inherent value in this process? Next, we will conduct in-depth analysis and exploration from three dimensions: technological innovation, economic benefits, and policy orientation.

2、 Enterprise microgrid construction-Enterprise level source network load storage collaboration solution
Energy cost optimization: Reduce electricity costs through strategies such as peak valley arbitrage, demand management, and green power substitution. For example, a manufacturing enterprise achieved over 60% of daytime photovoltaic power supply through microgrids, saving over 3 million yuan in annual electricity bills; The energy storage system participates in peak valley arbitrage, shortening the investment payback period to within 5 years;
Electricity market revenue: Aggregate distributed resources to participate in virtual power plant (VPP) trading, demand response, and ancillary service markets, and obtain additional revenue. If a certain park in Shanghai responds to the peak shaving demand of the power grid through microgrids, the annual income increase exceeds 2 million yuan;
Avoiding the risk of electricity price fluctuations: By achieving self-sufficiency in green electricity and regulating energy storage, we can reduce our dependence on high priced electricity from the power grid and hedge against the cost pressure caused by future price increases and carbon price hikes;
Direct carbon reduction: Integrating renewable energy sources such as photovoltaics and wind power to replace fossil fuel power generation significantly reduces Scope 2 carbon emissions. For example, the penetration rate of green electricity in a microgrid of a certain data center exceeds 80%, with an annual carbon reduction of 12000 tons;
Carbon asset appreciation: Accurately calculate carbon footprint, participate in carbon trading or meet supply chain carbon neutrality requirements. Apple, BMW and other companies have included supplier microgrid construction in their zero carbon procurement standards;
Policy dividend capture: Adapt to local policies such as solar energy storage subsidies and green electricity consumption quotas to reduce investment costs. Like the "Photovoltaic+Energy Storage" project in ZhejianghighestCan receive a 30% subsidy;
Enhanced power supply reliability: The ability to operate on isolated islands ensures uninterrupted power supply for critical loads, avoiding production losses caused by voltage drops and power outages (the semiconductor industry can suffer losses of up to * * in a single power outage);
Refined energy efficiency management: By optimizing the coordination of source, network, load, and storage through AI algorithms, the comprehensive energy efficiency has been improved by 15% to 30%. If a chemical enterprise uses microgrids to achieve cascade utilization of steam, electricity, and cold energy, the energy utilization rate will increase from 40% to 70%;
Extended equipment lifespan: Monitoring and managing power quality (such as harmonic suppression and voltage stability) to reduce equipment losses, extend production line lifespan, and lower maintenance costs;
Zero carbon supply chain empowerment: providing green power certification for upstream and downstream, helping to achieve carbon neutrality throughout the entire chain (such as CATL requiring suppliers to use green power to produce batteries);
Energy service innovation: Transforming from a single electricity user to an energy service provider through models such as energy custody and shared energy storage. For example, logistics parks sell low-priced green electricity to settled enterprises, creating new profit points;
Data Value Mining: Integrating energy data with production data to optimize production scheduling, equipment maintenance, and other aspects, achieving collaborative optimization of "energy efficiency production";
Promote the consumption of new energy: By flexibly adjusting and buffering energy storage, alleviate the pressure of the "duck curve" in the power grid, and improve the on-site consumption rate of new energy (some projects have a consumption rate of over 90%);
Supporting the stability of the power grid: participating in auxiliary services such as frequency and voltage regulation, becoming a "flexible node" of the new power system;
Promoting regional energy transformation: Microgrids in industrial parks can radiate to surrounding communities, forming a distributed energy network and accelerating the regional low-carbon process.

3、 Integrated project plan for source network load storage
3.1 Overview of Solutions
We have conducted multi-dimensional and multi angle real-time monitoring of distributed power sources, municipal power sources, energy storage devices, charging stations, and various loads in the enterprise microgrid. We have conducted energy data analysis, intelligent future forecasting, flexible resource scheduling, and strategic optimization and adjustment. Through the integrated real-time diagnosis and alarm system, we have facilitated coordinated interaction between dispatchable energy and load, and conducted in-depth energy situation analysis. This comprehensive plan closely meets the digital needs of enterprise microgrids in energy efficiency management, successfully achieving the intelligent transformation of safety assessment, dynamic adjustment of regulatory measures, and visual presentation of the overall situation. This solution can flexibly adapt to the interactive scenarios of various resources such as wind energy, solar energy, diesel power generation, energy storage, and charging facilities under multiple strategies, enabling the system to operate in an economically efficient state, thereby effectively reducing users' energy expenses and significantly improving the overall operational efficiency of enterprise microgrids.
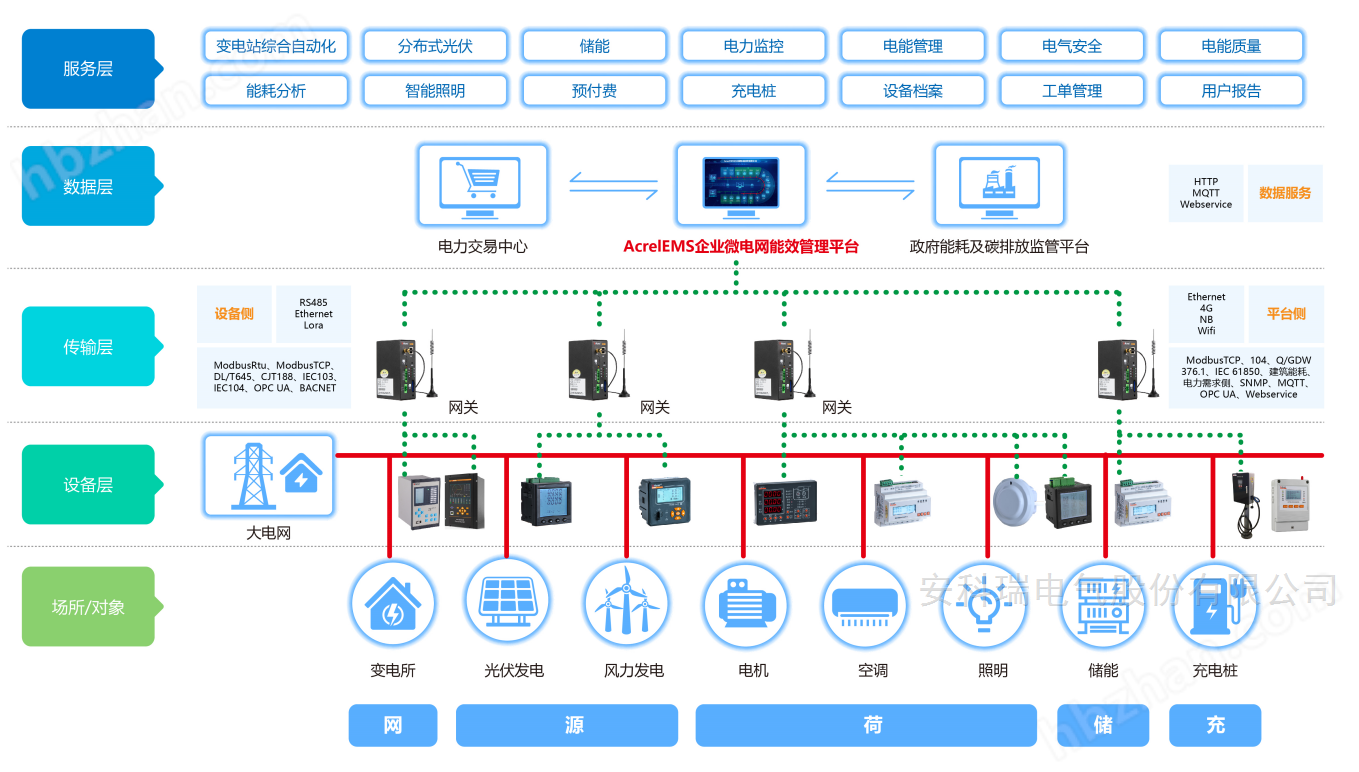
3.2 Solution Networking Architecture
The system covers the "source grid load storage charging" link of enterprise microgrids, collecting data from measurement and control devices, new energy generation, mains power, energy storage, charging piles, and conventional loads through intelligent gateways. It optimizes control based on load changes and grid scheduling, promoting the consumption of new energy while reducing the demand for the grid, making its operation safer and more efficient.

3.3 Core Functions of the Plan
Flexible expansion: When the short-term power consumption exceeds the capacity of the transformer, the energy storage can be quickly discharged to meet the energy requirements of the load;
Backup power supply: emergency power supply to ensure power quality;
Anti backflow: prevent the system power from being sent back to the grid and avoid assessment;
Peak shaving and valley filling: in conjunction with energy storage equipment, optimizing energy consumption costs with low charging and high discharging;
Demand control: energy storage, charge and discharge power tracking to prevent an increase in basic electricity bills;
Ordered charging: Guided by transformer capacity and electricity prices, utilizing technology to coordinate charging power and reduce operating costs;
Power prediction: prediction of power generation and electricity load, optimization of scheduling, and improvement of on-site consumption of new energy.

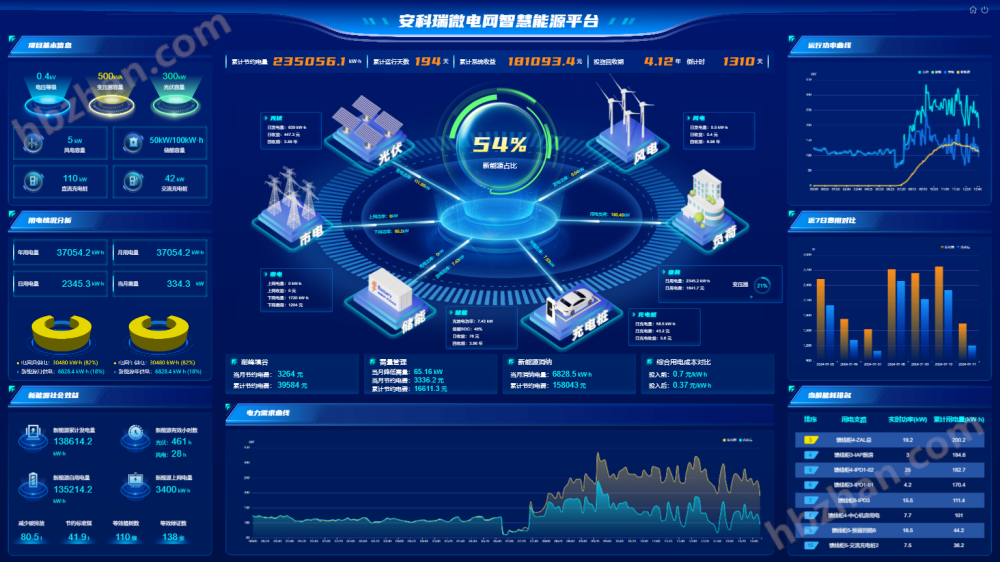
4、 Software feature interface display
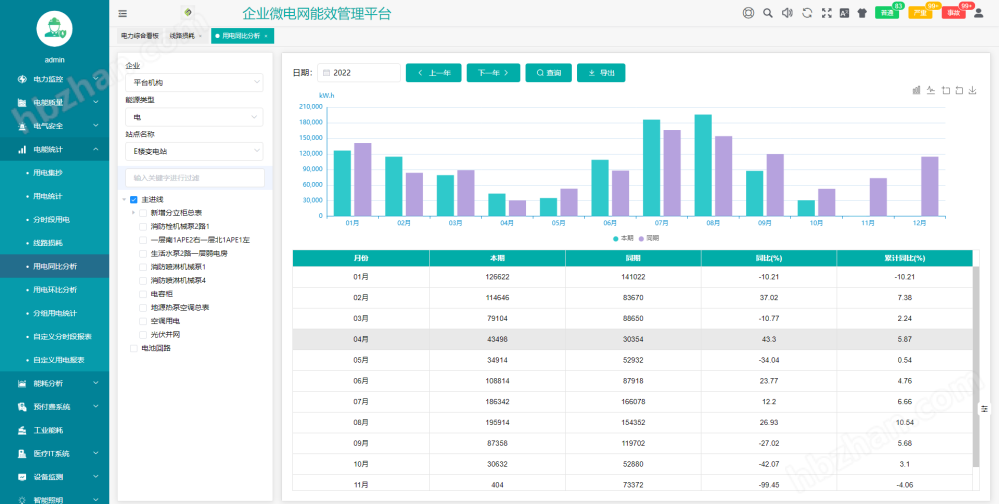
Electricity statistics: electricity consumption collection, electricity consumption statistics, time-based electricity consumption, line losses, year-on-year and month on month analysis of electricity consumption, grouped electricity consumption statistics, custom compound rates, time-based collection;
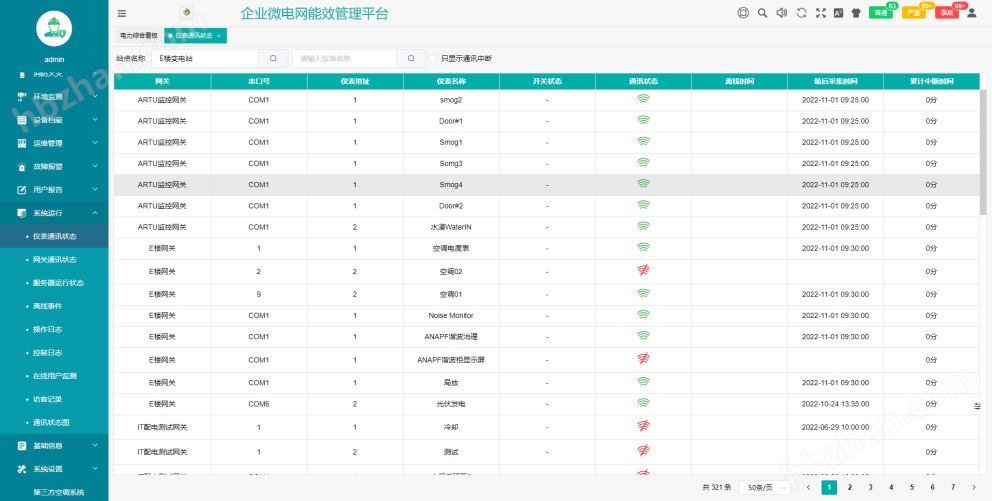
System operation: Instrument communication status, gateway communication status, server operation status, offline events, operation logs, control logs, online user monitoring, visitor records, communication status diagram;
Electrical safety: leakage and cable temperature measurement, electrical contact temperature measurement, contact temperature monitoring, contact temperature report, insulation monitoring, fiber optic equipment monitoring, fiber optic zone details, zone real-time data;

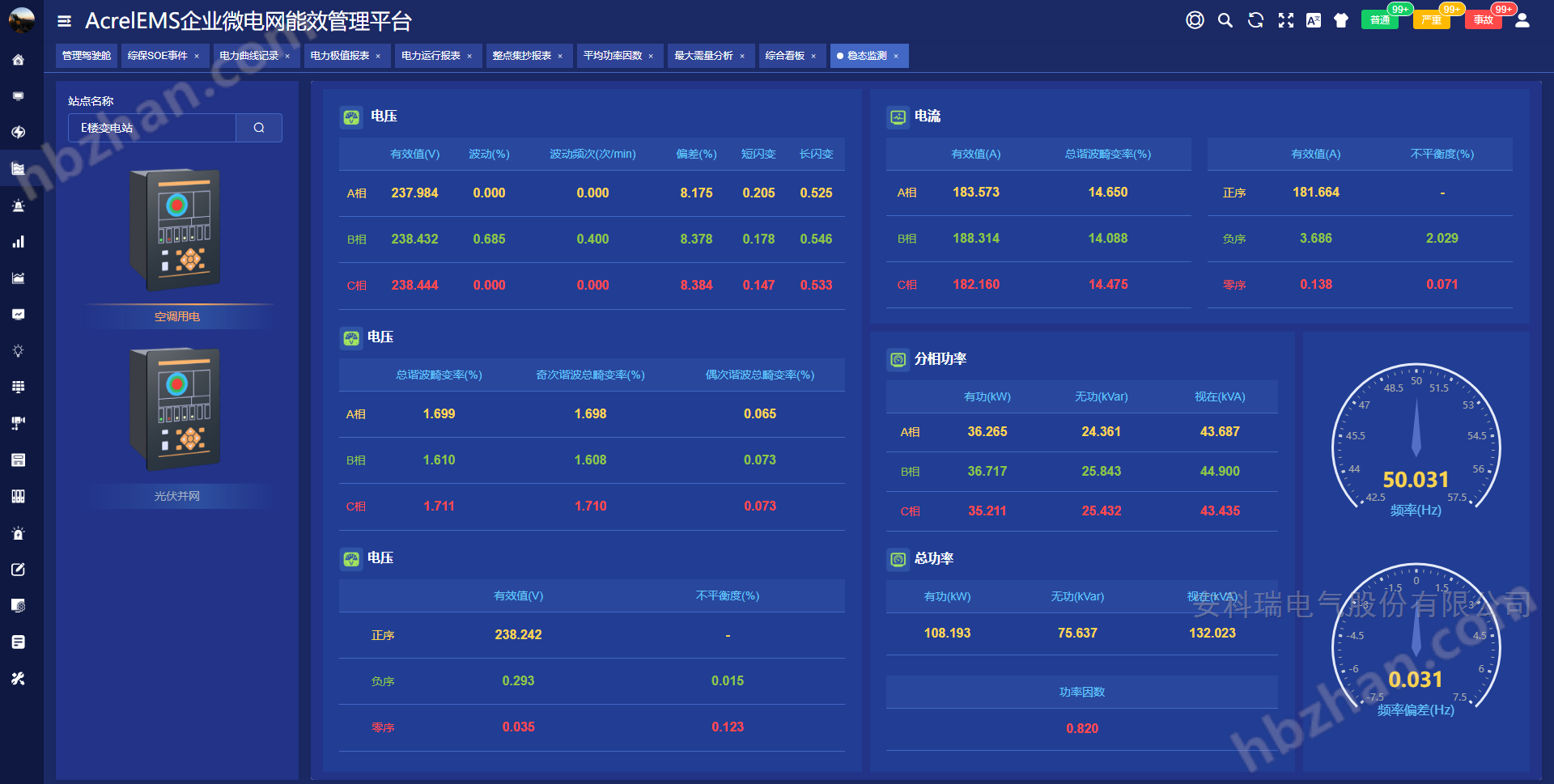
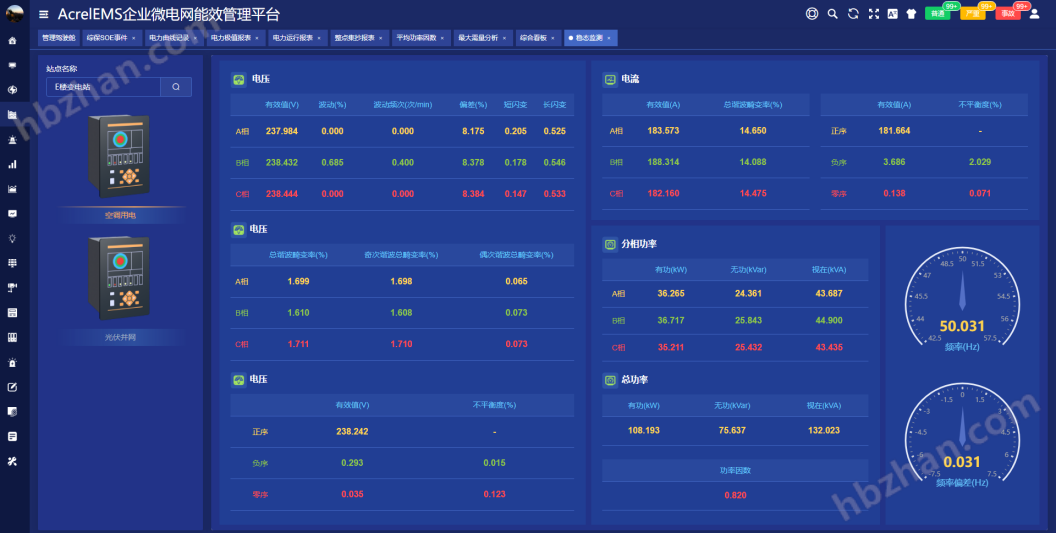
Power monitoring: power operation bulletin board, distribution room, DC screen monitoring, reactive power compensation cabinet, transformer monitoring, comprehensive protection S0E event, power curve recording, power report, power operation report, hourly collection report, hourly collection summary table, demand analysis, average power factor, harmonic analysis, harmonic spectrum, circuit monitoring, monthly power operation report, station load history rate, arc protection, partial discharge;

Distributed photovoltaics: comprehensive photovoltaic dashboard, power station operation monitoring, inverter operation monitoring, power station generation statistics, inverter generation statistics, photovoltaic power station distribution monitoring, inverter curve analysis, photovoltaic panels, multi device curve analysis, dispersion rate report, simulated power generation, inverter parameter alarm;

Power quality: comprehensive power quality dashboard, steady-state monitoring, harmonic spectrum, steady-state curve, harmonic curve, load curve, transient analysis, power quality SOE event and waveform analysis, power quality analysis, power quality governance, transient analysis report;
Intelligent lighting: intelligent lighting control, event control, lighting control, scene control, operation recording, scheduled tasks, lighting monitoring;

Energy storage module: energy storage operation and maintenance screen, energy storage dashboard, energy storage cabinet monitoring, equipment monitoring, statistical revenue report, time period revenue report, strategy issuance;

Industrial energy consumption: industrial energy consumption topology, production time setting, shift setting, trend analysis, carbon emission monitoring, electricity cost analysis, output input, output statistics, product input, unit consumption report, product unit consumption, unit consumption benchmarking analysis;

Carbon assets: emission reduction plan, carbon emission analysis, trading records, carbon trading records, carbon accounting list, quota accounting, carbon emission report, carbon flow chart, carbon emission assessment;

5、 Recommended hardware products
5.1 Monitoring, Protection, and Governance Products

5.2 Charging pile products